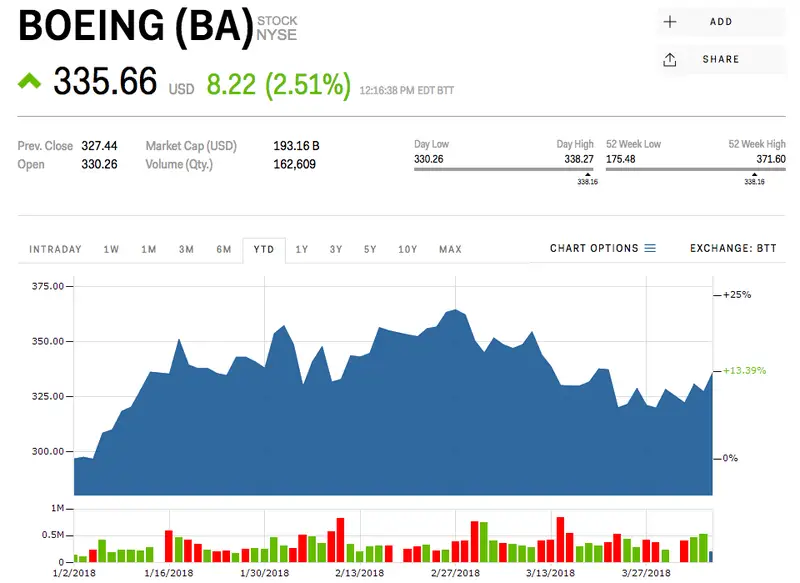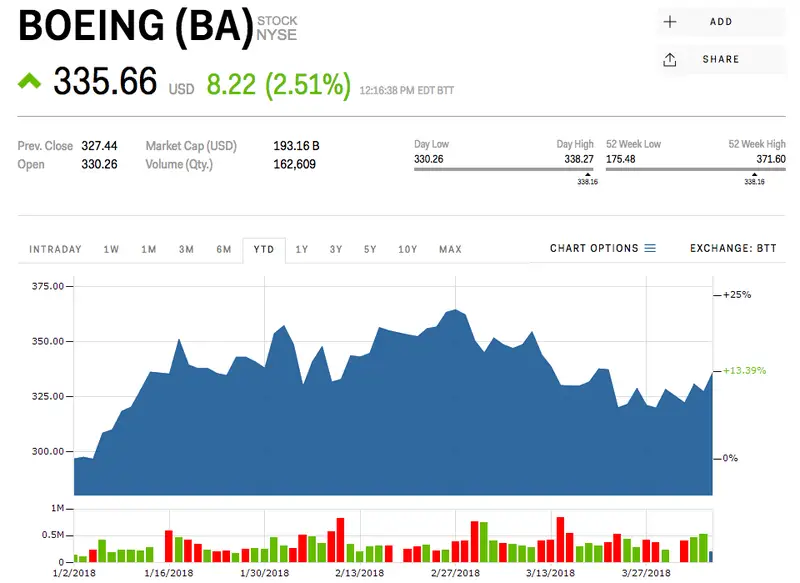
BA is the ticker symbol for The Boeing Company on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). It represents one of the most iconic aerospace companies in the world. Investors interested in aviation, defense, and high-tech manufacturing often keep a close eye on BA stock because of Boeing’s influence on both the commercial and defense sectors.
A Brief Overview of Boeing Company
Founded in 1916, Boeing has evolved into a global leader in aerospace manufacturing, producing commercial airplanes, defense systems, satellites, and more. Headquartered in Arlington, Virginia, Boeing’s operations span continents and cater to governments and corporations alike.
Boeing’s Historical Performance
Evolution Over the Decades
Boeing’s stock journey mirrors the aviation industry’s development. From the first commercial flights to modern space travel, Boeing has always been at the frontier. BA stock saw major gains during post-war aviation booms and took hits during global recessions and crises.
Key Milestones in Boeing’s Stock Journey
- 1960s: The jet age begins.
- 1997: Boeing merges with McDonnell Douglas.
- 2010s: The 787 Dreamliner launches.
- 2018-2019: The 737 Max tragedy shakes investor confidence.
- 2020-2021: The pandemic hits travel hard, crushing BA stock.
Factors Influencing BA Stock
Government Contracts and Defense Spending
Boeing’s significant share of U.S. defense contracts adds stability to its revenue. Fluctuations in defense budgets directly influence BA stock performance.
Commercial Aviation Trends
When airline companies flourish, Boeing benefits from aircraft orders. Conversely, high oil prices or reduced travel demand can reduce airline profits—and aircraft purchases.
Global Economic Impact
Boeing operates globally. Economic health in emerging markets can mean more aircraft sales. Recessions? Not so much.
Innovation and Technological Advancement
Cutting-edge R&D in fuel-efficient aircraft, autonomous systems, and space exploration projects all help push investor confidence up—if successful.
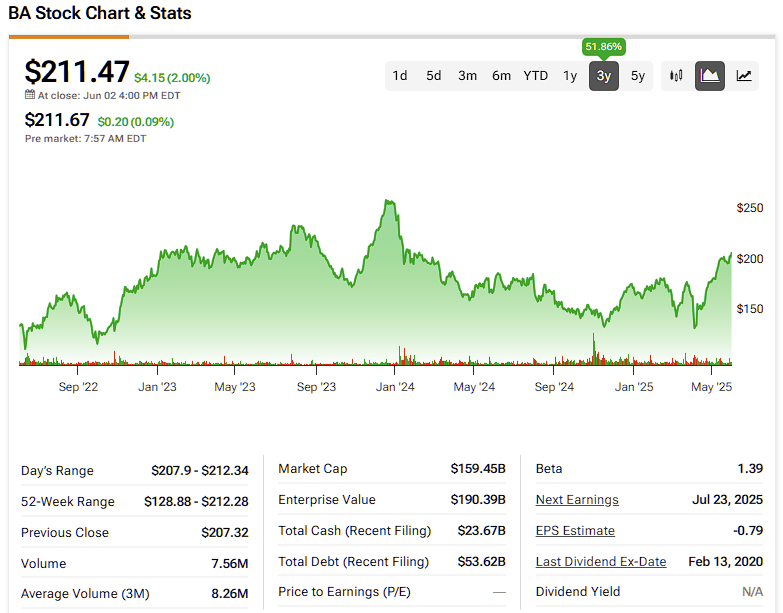
BA Stock in Recent Years
Impact of the 737 Max Crisis
The crashes of two 737 Max planes had devastating impacts. Grounding the aircraft globally led to billions in losses, lawsuits, and public trust issues.
COVID-19 Pandemic and Recovery
With grounded flights worldwide, demand for new aircraft plummeted. Boeing’s stock dropped from over $300 in 2019 to below $100 in 2020 before slowly recovering.
Supply Chain and Production Challenges
Component shortages, labor issues, and halted deliveries affected Boeing’s ability to rebound fully. These hiccups continue to cause volatility in BA stock.
Boeing’s Financial Health
Revenue Streams and Profitability
Boeing earns from commercial airplanes, defense, and global services. However, profitability has taken a hit post-737 Max and during the pandemic.
Debt and Cash Flow Analysis
To stay afloat during hard times, Boeing increased its debt significantly. Watching how Boeing manages and repays this debt is key for investors.
Key Financial Ratios to Watch
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio
- Debt-to-Equity ratio
- Free Cash Flow
- Operating Margins
Competitive Landscape
Boeing vs Airbus
Boeing’s biggest rival is Airbus. Both companies compete fiercely in commercial aviation. While Boeing leads in defense, Airbus has gained significant ground commercially.
Role of Emerging Players
Companies like COMAC (China) and Embraer (Brazil) are nibbling at Boeing’s market. They may not be direct threats yet, but the landscape is shifting.
Industry Consolidation and Partnerships
Strategic alliances and joint ventures, such as with NASA or DARPA, offer Boeing long-term growth avenues and competitive defense advantages.